An aspirated in-syringe device fixed with ionic liquid and β-cyclodextrin-functionalized CNTs/TiO2 for rapid adsorption and visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity
Abstract
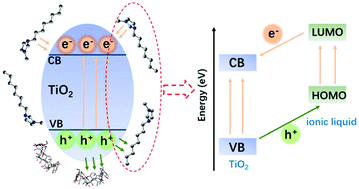
In this paper, the ionic liquid (IL), 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([Omim][PF6]), was employed to synthesize β-cyclodextrin (β-CD)-functionalized carbon nanotubes/TiO2 (IL–CD-CNTs/TiO2) nanocomposite via a one-pot solvothermal process. The as-prepared product was characterized by SEM, TEM, XRD, TG, FT-IR, EIS, and so forth. Coupled with an aspirated in-syringe device, IL–CD-CNTs/TiO2 could yield the rapid removal of water contaminants within 8 min. In addition to the excellent adsorption capacity, this dual-functional photocatalyst also showed enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light at a degradation rate of 97% within 180 min. The photocatalytic mechanism based on the formation of the inclusion complex, density functional theory, and electronic structure of IL–CD-CNTs/TiO2 was comprehensively discussed. The IL not only served as the reaction medium but also played a crucial role in improving the adsorption capacity and photocatalytic activity. By exhibiting a strong electron-donating character, IL could promote efficient charge transfer, inhibiting the recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs. The as-prepared photocatalyst—capable of rapid adsorption and photodegradation—can meet the requirements of practical applications and reveals a promising direction toward wastewater treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...