Retracted Article: PEDOT/NiFe2O4 nanocomposites on biochar as a free-standing anode for high-performance and durable microbial fuel cells†
Abstract
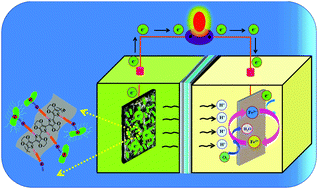
Biochar (BC), prepared from the carbonization of neem wood, was modified with nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nanorod/poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) composite and directly employed as a free-standing and binder-free anode in microbial fuel cells (MFCs). The morphological and X-ray diffraction analyses demonstrate that the cubic spinel-structured NiFe2O4 nanorods are homogeneously distributed over the sheet-like amorphous PEDOT. The bioelectrochemical activity of exoelectrogens is improved with PEDOT/NiFe2O4/BC as endorsed by the superior oxidation current in the voltammograms. Furthermore, the MFC with PEDOT/NiFe2O4/BC demonstrates a peak power of 1200 mW m−2 because of the unique catalytic nanoarchitectures, compact biofilm formation, continuous electron conduction paths, and elevated structural and chemical stabilities of PEDOT/NiFe2O4. The waste matter-derived electrode constituent, binder-free electrode modification, mediator-less electron transference, and considerable power generation associated with a proficient lifespan performance of PEDOT/NiFe2O4 open up a versatile avenue towards the development of cost-efficient, high-performance, and durable MFCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...