Hydrothermal synthesis of carbon nanodots from bovine gelatin and PHM3 microalgae strain for anticancer and bioimaging applications†
Abstract
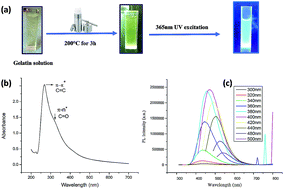
Semi-conductor quantum dots (QDs) are favorite candidates for many applications especially for potential use as optical bioimaging agents. But the major issue of QDs is toxicity. In the present study, carbon nanodots were synthesized using a green hydrothermal approach from gelatin protein using a previously established protocol. However, the PL properties and applications of the as-synthesized CG (bovine gelatin) nanodots were remarkably different from those of previously reported gelatin carbon dots. CG (bovine gelatin) nanodots had sizes greater than the Bohr exciton radius but still had QD like fluorescence characteristics. Furthermore, the results from fluorescence spectroscopy demonstrated a tunable PL emission profile at various excitation wavelengths. Second, carbon nanodots were also synthesized from algal biomass of Pectinodesmus sp. via a green hydrothermal approach, denoted as CA (PHM3 algae) nanodots. A study of the PL properties and surface chemical composition of CG (bovine gelatin) and CA (PHM3 algae) nanodots suggested that the surface chemical composition significantly alters the surface states which directly influence their PL properties. CG (bovine gelatin) nanodots were used for imaging of plant and bacterial cells with good imaging sensitivity comparable to toxic semiconductor quantum dots. Moreover, the results from in vitro studies suggested good anticancer properties of CA (PHM3 algae) and CG (bovine gelatin) nanodots with minimum GI50 values of 0.316 ± 0.447 ng ml−1 (n = 2) and 8.156 ± 6.596 ng ml−1 (n = 2) for HCC 1954 (breast cancer) and 0.542 ± 0.715 ng ml−1 (n = 2) and 23.860 ± 14.524 ng ml−1 (n = 2) for HCT 116 (colorectal cancer) cell lines, respectively.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Quantum and carbon dots


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...