Optimization of analytical conditions for precise and accurate isotope analyses of Li, Mg, Fe, Cu, and Zn by MC-ICPMS
Abstract
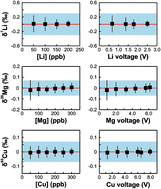
Analytical advances in Multi-Collector Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (MC-ICPMS) over the past decade have led to rapid growth in studies utilizing non-traditional stable isotopes. There are substantial analytical challenges for achieving precise and accurate measurements of these isotopes that limit their applications in geoscience where natural isotopic variations are generally small. Here, we evaluate experimental factors that may affect the accuracy and repeatability of isotopic measurements of selected stable metal isotopes (Li, Mg, Fe, Cu, and Zn) on a Nu Plasma II MC-ICPMS to provide optimized analytical protocols for acquiring high quality data. Our results suggest that the repeatability level (2SD) that is readily obtainable for δ7Li is ±0.09‰ to ±0.24‰, for δ26Mg is ±0.03‰ to ±0.07‰, for δ56Fe is ±0.05‰ to ±0.07‰, for δ65Cu is ±0.03‰ to ±0.05‰, and for δ66Zn is ±0.02‰ to ±0.04‰. Instrumental mass bias for these isotope systems can be corrected adequately using the standard–sample bracketing method but it requires that target elements are of high purity, a close match in analyte concentrations between samples and bracketing standards, and preparation of all running solutions using the same concentration of nitric acid. Overall, the Nu Plasma II is well suited for precise and accurate analyses of the isotopes studied here, and the optimal results were obtained using a ‘wet’ plasma operating at a normal radio-frequency (RF) power.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...