Determination of antimony in water samples by hydride generation coupled with atmospheric pressure glow discharge atomic emission spectrometry
Abstract
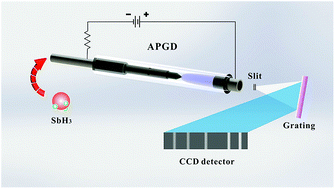
A low power (∼10 W), miniaturized atmospheric pressure glow discharge (APGD) source sustained between a tungsten cathode and a titanium tube anode was coupled with a hydride generation (HG) system for sensitive determination of antimony in water samples with atomic emission spectrometry (AES). Sb ions were converted into volatile hydrides through the reaction with KBH4 firstly and then were introduced into the APGD source for excitation and detected using a compact CCD (charge-coupled device) microspectrometer. A univariate approach was used to achieve optimized conditions and derive analytical figures of merit. Under optimal conditions, the limits of detection and quantification for Sb were 0.14 and 0.5 μg L−1, respectively. Moreover, the HG-APGD-AES system offered good repeatability (relative standard deviation < 1.5%). The calibration curve was linear in the range between 0.5 and 100 μg L−1, with a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.9996. The proposed method was successfully applied to the determination of certified reference materials (GSB 07-1376-2001, GBW07305a, GBW07307a and GBW073066) and some groundwater samples. Recoveries of Sb added to these water samples were within 90.9–100.7%, proving the good accuracy of the HG-APGD-AES method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...