Diol pretreatment to fractionate a reactive lignin in lignocellulosic biomass biorefineries†
Abstract
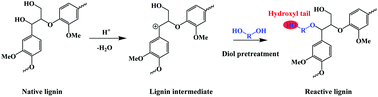
Lignin-first fractionation has become a new biorefinery target to obtain valuable lignin monomers toward the complete utilization of lignocellulosic biomass, but increasing delignification through conventional pretreatment approaches often affects the structural integrity of the dissociated lignin. We discovered a new reactive lignin with a great solvent solubility and preserved β-O-4 linkages from eucalyptus after a modified organosolv pretreatment using 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO). Unlike conventional organosolv pretreatment using ethanol, lignin deposition was not observed in 1,4-BDO pretreatment. Meanwhile, 2D HSQC NMR analysis revealed that the residual lignin obtained from 1,4-BDO pretreated eucalypts contained a relatively higher amount of β-O-4 interunit linkages, indicating its higher integrity than ethanol pretreated lignin. This result agreed with the lower content of phenolic hydroxyl groups in dissolved lignin via31P NMR analysis. With increasing pretreatment severity, the amount of aliphatic hydroxyl groups decreased in ethanol pretreated lignin while it remained at a higher level in 1,4-BDO pretreated lignin. These results suggested that 1,4-BDO quenched the benzyl carbocation intermediate and formed ether linkages with a hydroxyl tail at the α position of the lignin. Solubility tests revealed that grafting aliphatic hydroxyl groups on 1,4-BDO lignin increased its dissolution. This phenomenon was further demonstrated for four different diols with similar structures. In addition, more than 90% cellulose conversion was obtained for all the diol pretreated eucalyptus after 48 h of enzymatic hydrolysis with cellulase at a loading of 7.5 FPU per gram of glucan. Diol pretreatment thus offers a promising reaction pathway to coincide with three pillars of biorefinery for lignin fractionation, lignin structural integrity, and cellulose hydrolysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...