One-pot conversion of lysine to caprolactam over Ir/H-Beta catalysts†
Abstract
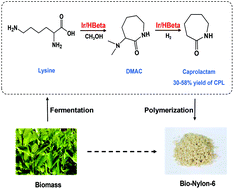
Amino acid lysine could serve as an ideal bio-based feedstock for the synthesis of caprolactam (CPL), which is currently a petroleum-derived monomer. Herein, we report the one-pot conversion of L-lysine to CPL via hydrogenolysis over bifunctional metal supported catalysts. Among the various hydrogenation metals and different supports, the combination of Ir and HB zeolite gave the best performance. Under optimal conditions, a 30% yield of CPL from L-lysine and a 58% yield from the reaction intermediate α-dimethyl amino caprolactam (DMAC) were obtained over a 2Ir/HB-124 catalyst at 250 °C in an autoclave or fixed-bed reactor. The reaction solvent dramatically affected the reaction selectivity, and methanol was found to be the best due to its unique contribution towards the formation of α-dimethyl amino caprolactam (DMAC) as well as the following C–N breakage of the C–N(CH3)2 bond. The acid sites on the catalyst accelerate lactam formation, and the synergy between the acid sites and hydrogenation sites favours C–N bond hydrogenolysis to produce CPL. Besides the acidity, the large pore size of HB is able to accommodate big reaction intermediate molecules inside the pores further ensures the superior performance of Ir/HB. The reaction route was identified, i.e., L-lysine first undergoes cyclization and N-methylation to DMAC, and then C–N(CH3)2 bond hydrogenolysis to form CPL. The Ir/HB catalyst has reasonably good stability and high selectivity, making this one-pot conversion process a novel and environmentally benign way of producing CPL from easily available renewable feedstocks.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...