Antimetastatic effects of gossypol on colon cancer cells by targeting the u-PA and FAK pathways
Abstract
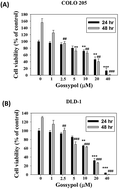
Metastasis is the most prevalent cause of treatment failure in patients with colon cancer. Gossypol is reported to exhibit antioxidant, anticancer, antivirus and antimicrobial properties. However, the effects of gossypol on cancer invasion and tumour growth of human colon cancer remain unclear. This study aimed to provide molecular evidence associated with the antimetastatic and anti-tumour effects of gossypol on human colorectal carcinoma (CRC) cells. Gossypol inhibited the viability of human colon cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner. Gossypol was sufficient to reduce the invasion, migration and adhesion in DLD-1 and COLO 205 cells. Zymography and western blot assay showed that gossypol reduced the activities and protein expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (u-PA), respectively. Gossypol suppressed the level of p-focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers, including N-cadherin, fibronectin and vimentin. Gossypol also inhibited the lung metastasis of DLD-1 cells, as indicated by the nude mouse model. These results suggested that gossypol inhibited the metastatic properties of human colon cancer cells by targeting u-PA through the FAK pathway, suggesting that gossypol could be used as an adjuvant therapeutic agent for the treatment of human colon cancer cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...