Characterization of polymethoxyflavone demethylation during drying processes of citrus peels†
Abstract
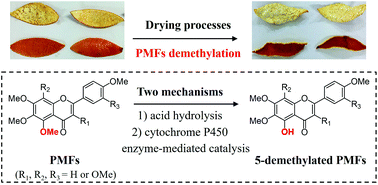
Polymethoxyflavones (PMFs) are found almost exclusively in citrus peel and have attracted much attention due to their potential health benefits. Dried citrus peel is an important ingredient for applications in food and traditional Chinese medicine. However, the structural changes of PMFs during drying processes of citrus peel remain unknown. In this study, for the first time we discovered that four major permethoxylated PMFs, i.e. sinensetin, nobiletin, heptamethoxyflavone and tangeretin, underwent demethylation at the 5-position on the A ring of their flavonoid structures to yield corresponding 5-demethylated PMFs during the drying process of citrus peel. Our results further demonstrated that the aforementioned PMF demethylation was through two mechanisms: acid hydrolysis and enzyme-mediated catalysis. PMF demethylation in citrus peels was systematically characterized during hot-air drying (HAD), vacuum-freeze drying (VFD) and sun drying (SD). The highest PMF demethylation was obtained in SD followed by HAD and VFD. This study provided a solid scientific basis for rational control of PMF demethylation in citrus peels, which could facilitate the production of high-quality citrus peel and related products.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...