Active sites and mechanism of the direct conversion of methane and carbon dioxide to acetic acid over the zinc-modified H-ZSM-5 zeolite†
Abstract
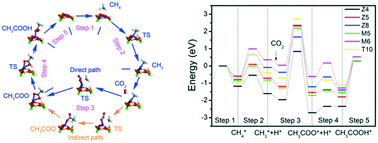
Conversion of CH4 and CO2 to higher value chemicals will contribute to alleviating green-house gas emissions and the global fossil fuel shortage. Introducing metals into zeolites is used to catalytically convert CH4 and CO2 to acetic acid. Understanding the local structure of active sites and their functions in reaction mechanisms will help the design of highly-efficient catalysts and promote further application. In the present work, the effect of the local structure of active sites on the conversion of CH4 and CO2 over Zn modified H-ZSM-5 zeolites has been studied systematically using density functional theory. Herein, two different Zn-modified H-ZSM-5 structures are considered, one containing isolated Zn2+ cations and the other small ZnO clusters. It is found that the catalytic activity of the conversion of CH4 and CO2 is strongly dependent on the local structure of the active sites. Zn2+ cations located in the 5-membered rings of the sinusoidal and straight channels exhibit better catalytic activity than other isolated Zn2+ sites and small ZnO clusters due to the favorable adsorption properties of reactants and activation energies. The rate-determining step of the whole process on the isolated 5-membered Zn2+ in the sinusoidal channel is the insertion of CO2 into the Zn–CH3 bond, while that on the isolated 5-membered Zn2+ in the straight channel is the desorption of acetic acid.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...