Stoichiometric active site modification observed by alkali ion titrations of Sn-Beta†
Abstract
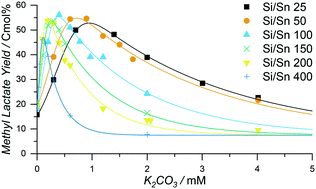
Sn-Beta zeolite can convert carbohydrate feedstocks through different pathways into a variety of chemical building blocks. Alkali salts influence the selectivity between these pathways, but the details of the alkali ion effect on the catalyst remain unclear. Here, we combine the systematic variation of tin content in Sn-Beta zeolite with alkali ion titrations and functional assays to assess the stoichiometry of alkali binding and the prospect of predicting operation optima from catalyst properties. This approach is used to evaluate the product selectivity of defined catalyst states for the conversion of glucose into methyl lactate and to characterise the catalytic behavior of active sites with respect to the degree of titration. The optimum selectivity to methyl lactate was found at similar ratios of alkali and active tin for catalysts of different tin loadings, indicating a stoichiometric correlation between added alkali ions and tin content in the Sn-Beta zeolite. The observations also indicate that double dissociation of the active site occurs and that titration between three states is possible. The protonated form of Sn-Beta has a poor methyl lactate selectivity, whereas a single exchange of a proton with potassium at the active site leads to a catalytic form with a very high selectivity, while a double exchange leads to a catalytically inactive state of the active site. Exchange phenomena at the active site were corroborated by FT-IR spectroscopy, which showed that potassium interacts with hydroxyl groups in the vicinity of Sn.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...