Deviations from Beer's law on the microscale – nonadditivity of absorption cross sections
Abstract
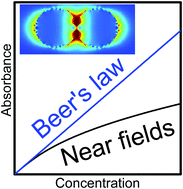
Beer's law assumes a linear dependence of absorbance on concentration, accordingly the index of absorption and the molar attenuation coefficient are material properties and the absorption cross section, including absorbance itself, must be additive if chemical interactions are excluded. Under the “no interaction” condition, a linear dependence should also exist between macroscopic polarization and the number of induced dipole moments per unit volume. The latter linear dependence is the basis for dispersion theory. Invoking Maxwell's wave equation, Beer's law has been derived recently from dispersion theory. As a result, Beer's law is a limiting law. Accordingly, indices of absorption and molar attenuation coefficients including absorption cross sections are no material properties and the latter can per se not be additive. Indeed, as we show in this contribution, not even for particles very small compared to wavelength, where the scattering cross sections can be neglected, is this additivity a given, except for comparably large distances between the particles. We investigate the magnitude of these critical distances with the help of finite difference time domain calculations for amorphous SiO2 spheres in the infrared spectral range. Based on electric field maps, we conclude that the deviations scale with oscillator strengths and, correspondingly, with local electric fields and nearfield effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...