The mechanism and rate constants for oxidation of indenyl radical C9H7 with molecular oxygen O2: a theoretical study†
Abstract
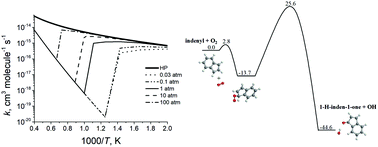
Ab initio G3(MP2,CC)//B3LYP/6-311G(d,p) calculations have been carried out to map out the C9H7O2 potential energy surface in relation to the reaction of the 1-indenyl radical with molecular oxygen. The resulting energetics and molecular parameters of the species involved in the reaction have been then utilized in Rice–Ramsperger–Kassel–Marcus master equation calculations of temperature- and pressure-dependent reaction rate constants and product branching ratios. The results demonstrate that, while the reaction is insignificant at low temperatures, at higher temperatures, above 800 K or higher depending on the pressure, the prevailing reaction channel leads to the formation of the 1-H-inden-1-one + OH products via a 1,3-H shift from C to O in the initial association complex W1 accompanied by OH elimination through a high barrier of 25.6 kcal mol−1. The branching ratio of 1-H-inden-1-one + OH increases from ∼61% to ∼80% with temperature, whereas c-C6H4-CH2CHO + CO (32–12%) and coumarin + H (7–6%) are significant minor products. The total rate constant of the indenyl + O2 reaction leading to the bimolecular products is independent of pressure and exceeds 1.0 × 10−15 cm3 molecule−1 s−1 only at temperatures above 2000 K, reaching 6.7 × 10−15 cm3 molecule−1 s−1 at 2500 K. The indenyl + O2 reaction is concluded to be too slow to play a substantial role in oxidation of the five-member ring in indenyl and the present results corroborate the assertion that molecular oxygen is not an efficient oxidizer of five-member-ring radicals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...