Distinctive phase separation dynamics of polymer blends: roles of Janus nanoparticles†
Abstract
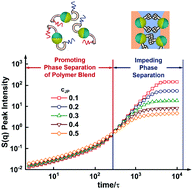
Janus nanoparticles (JPs), which are anisotropic nanoparticles with at least two opposite surface regions, have been demonstrated as highly efficient compatibilizers for polymer blends. However, there are still a number of open questions concerning the mechanism behind the influence of JPs on the phase separation dynamics of polymer blends. Herein, we report a counter-intuitive feature of JPs concerning their roles during spinodal decomposition (SD); that is, they promote the decomposition of unlike polymers in the early stage of SD but retard it during the late stage. This is in remarkable contrast to traditional compatibilizers such as block copolymers and homogenous nanoparticles, which impede phase separation during both stages. We further demonstrate that the unique promoting effect of JPs at early times is due to the formation of microphase-separated homopolymer-rich regions in the vicinity of opposite JP surface regions. Our findings are expected to have important implications for the phase separation behavior of JP-compatibilized polymer blends, whose morphologies and performance could be controlled by tuning the interactions between the constituent polymers and JP-based compatibilizers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...