Evolution of crystal growth in MgO–Al2O3–SiO2 glass ceramics†
Abstract
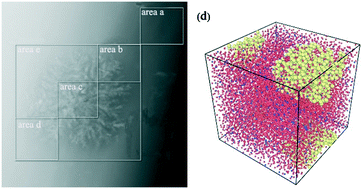
It is a necessary part of crystal design to explore the process through which crystals precipitate in glass ceramics. In this work, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to structurally characterize a glass of composition 20MgO–20Al2O3–54SiO2–3K2O–1Fe2O3–2TiO2 (mol%). The evolution of the glass–crystal interface during the crystallization process was investigated using energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDXS) in scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) mode. Results showed that alkaline-earth metal Mg aggregated at the interface during crystallization to form an Mg-enriched layer, which could be verified through the concentration formula. According to the results of molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, the difference in diffusion coefficients between the base glass and Mg-enriched layer leads to the formation and stabilization of the layer. MD simulation also indicated that there was aggregation of Al in the enriched layer, which inhibited further crystal growth.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...