PDMS-coated hypercrosslinked porous organic polymers modified via double postsynthetic acidifications for ammonia capture†
Abstract
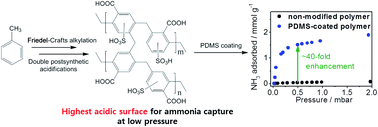
A hypercrosslinked porous organic polymer was modified by post-oxidation and post-sulfonation to obtain a porous platform with a high density of acidic groups. Such an acidified material exhibits record high NH3 adsorption capacity per surface area, fast adsorption rate, and recyclability at low desorption temperature. Noticeably, the coating of the polymer with PDMS represents a facile and efficient route to enable both a significant improvement of low-pressure NH3 adsorption capacity (∼40-fold enhancement; from 0.04 to 1.41 mmol g−1) with respect to the non-modified polymer at 500 ppm and hydrophobicity associated with the selective sorption of NH3 over water vapor (hydrophilic for the non-coated material). This material is easy to prepare, cost-effective, and scalable to mass production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...