Intensification of esterification through emulsification: isolation of dilute low molecular weight carboxylic acids
Abstract
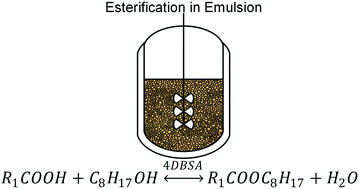
A concept for isolation of low molecular weight carboxylic acids (e.g., acetic acid) from dilute aqueous streams was developed. This concept of combining chemical conversion of the carboxylic acids with in situ liquid–liquid extraction enhanced by catalysis and emulsification was proven applicable for carboxylic acid concentration of 1 mol l−1. Chemical conversion was achieved by esterification with 1-octanol, catalysed by the surfactant 4-dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid. Emulsification induced by the catalyst was confirmed to be essential for high conversion and separation efficiency. Investigations were supported and evaluated by design of experiments and yielded conversions beyond 54.3% and separation efficiencies beyond 57.5% for acetic acid. Evaluation of process parameters yielded a quadratic model for prediction of process performance. Applicability of the concept for formic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid isolation from aqueous feed was confirmed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...