Enhancement of Fe–N–C carbon catalyst activity for the oxygen reduction reaction: effective increment of active sites by a short and repeated heating process†
Abstract
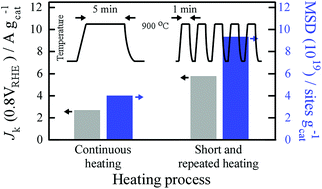
Controlling the formation of Fe–N–C catalytic sites is crucial to activate the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) for realization of non-precious electrocatalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). We present a quantitative study on the effect of a newly obtained thermal history on the formation of Fe–N–C catalytic sites. A short and repeated heating process is employed as the new thermal history, where short heating (1 min) followed by quenching is applied to a sample with arbitrary repetition. Through electrochemical quantitative analysis, it is found that the new process effectively increases the Fe–N–C mass-based site density (MSD) to almost twice that achieved using a conventional continuous heating process, while the turn-over frequency (TOF) is independent of the process. Elemental analysis shows that the new process effectively suppresses the thermal desorption of Fe and N atoms during the initial formation stage and consequently contributes to an increase in the Fe–N–C site density. The resultant catalytic activity (gravimetric kinetic current density (0.8 V vs. RHE)) is 1.8 times higher than that achieved with the continuous heating process. The results indicate that fine control of the thermal history can effectively increase the catalytic activity and provide guidelines for further activation of non-precious ORR electrocatalysts for PEMFCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...