Towards cancer diagnostics – an α-feto protein electrochemical immunosensor on a manganese(iv) oxide/gold nanocomposite immobilisation layer
Abstract
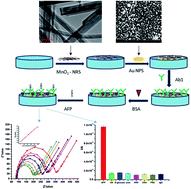
A novel electrochemical immunosensor for the quantification of α-feto protein (AFP) using a nanocomposite of manganese(IV) oxide nanorods (MnO2NRs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) as the immobilisation layer is presented. The MnO2NRs was synthesised using a hydrothermal method and AuNPs were electrodeposited on a glassy carbon electrode surface. The MnO2NRs were characterised with scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were used to characterise the immunosensor at each stage of the biosensor preparation. The MnO2 nanorods and AuNPs were applied as the immobilisation layer to efficiently capture the antibodies and amplify the electrochemical signal. Under optimised conditions, the fabricated immunosensor was utilised for the quantification of AFP with a wide dynamic range of 0.005 to 500 ng mL−1 and detection limits of 0.00276 ng mL−1 and 0.00172 ng mL−1 (S/N = 3) were obtained from square wave anodic stripping voltammetry and EIS respectively. The nanocomposite modifier enhanced the immunosensor performance. More so, this label-free immunosensor possesses good stability over a period of two weeks when stored at 4 °C and was selective in the presence of some interfering species.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...