Effects of riboflavin and AQS as electron shuttles on U(vi) reduction and precipitation by Shewanella putrefaciens
Abstract
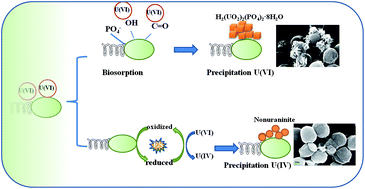
Understanding the mechanisms for electron shuttles (ESs) in microbial extracellular electron transfer (EET) is important in biogeochemical cycles, bioremediation applications, as well as bioenergy strategies. In this work, we adapted electrochemical techniques to probe electrochemically active and redox-active Shewanella putrefaciens. This approach detected flavins and humic-like substances of Shewanella putrefaciens, which were involved in electron transfer to the electrode. A combination of three-dimensional excitation-emission (EEM) florescence spectroscopy methods identified a mixture of riboflavin and humic-like substances in supernatants during sustained incubations. The reductive behaviour of U(VI) by Shewanella putrefaciens in the presence of riboflavin (RF) and anthraquinone-2-sulfonate (AQS) was also investigated in this study. The results indicated that RF and AQS significantly accelerated electron transfer from cells to U(VI), thus enhancing reductive U(VI). The precipitate was further evidenced by SEM, FTIR, XPS and XRD, which demonstrated that chernikovite [H2(UO2)2(PO4)2·8H2O] became the main product on the cell surface of S. putrefaciens. In a contrast, U(IV) mainly existed amorphously on the cell surface of S. putrefaciens with added RF and AQS. This work has significant implications in elucidating RF and AQS as electron shuttles that are efficient in reduction of uranium in geological environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...