Exploration and development of gold- and silver-catalyzed cross dehydrogenative coupling toward donor–acceptor π-conjugated polymer synthesis†
Abstract
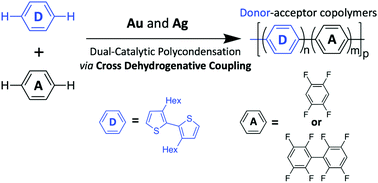
π-Conjugated polymers are materials of interest for use in organic electronics. Within these polymers, donor–acceptor polymers are favorable for solar cell applications due to improved charge mobility, better absorption in the low energy region of the solar spectrum, and tunable band gaps. One of the barriers to commercializing these donor–acceptor materials is that their synthetic pathways are complex because of the alternating repeat units in the polymer. To address this, the application of cross dehydrogenative coupling (also called oxidative CH/CH cross-coupling) toward the synthesis of donor–acceptor polymers was explored. In this work, the roles of specific reagents in a one-pot gold- and silver-catalyzed cross dehydrogenative coupling and the factors that contribute to selectivity for cross-coupling rather than homo-coupling are analyzed. Based on our results, we postulate that the percentage of alternating repeat units in the final polymer is affected by the increased reactivity of the dimer that forms in the initial stages of the polymerization compared to the monomer, which ultimately may be exploited to control the ratio of electron-rich to electron-poor monomers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...