Poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine)-based biodegradable nanogels for controlled drug release
Abstract
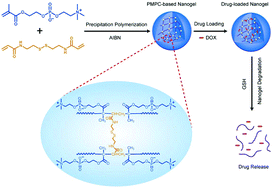
Stimulus responsive nanogels have great potential in the application of drug delivery. In this work, biodegradable zwitterionic poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) (PMPC) nanogels were fabricated by the reflux precipitation polymerization, which was clean and convenient for the application of drug delivery. The hydrodynamic size of the obtained PMPC nanogels was below 200 nm with a narrow size distribution (polydispersity index below 0.1). Moreover, the nanogels showed excellent protein adsorption resistance and remained stable at high concentrations of salt. Furthermore, the PMPC nanogels exhibited redox-responsive performance, and the degradation rate of the nanogels increased as the concentration of glutathione and the pH value increased. In addition, the nanogels could be fully disrupted into short linear polymers (Mw = 2000 g mol−1) after 24 h degradation. The doxorubicin-loaded nanogels showed low drug leakage under physiological conditions (below 15% in 24 h), while they presented rapid drug release in a reduction environment (above 80% in 24 h). The cell cytotoxicity assays revealed that the blank zwitterionic nanogels were nontoxic to the human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cells (A549 cells) even at high concentrations (1 mg mL−1), while the DOX-loaded nanogels showed efficient inhibition to the tumor cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...