Experimental validation of a computationally-designed tiotropium membrane sensor†
Abstract
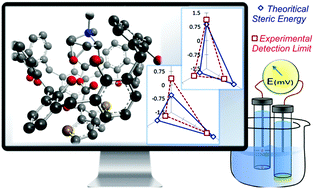
In this study we draw parallel computational and experimental data for potentiometric sensor assembly. Tiotropium (TIO) is a long acting anticholinergic agent and is used for maintenance treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Systems comprising different ion exchangers with or without ionophores were theoretically and practically evaluated for TIO membrane sensors. Different phenyl borate derivatives as cation exchangers along with calix[8]arene or (2-hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin as ionophores were compared in terms of steric energies and detection limits. Tetrakis-[3,5-bis(trifluoro-methyl)phenyl] borate and calix[8]arene sensors provided the lowermost steric energy (−30.63 kcal mol−1) as well as detection limit (1.6 × 10−7 mol L−1) for TIO analysis. Correlation between the normalized values of theoretical energies and practical detection limits was reasonably close; therefore, molecular mechanics offers a viable alternative to experimental optimization of sensor assembly. The optimized sensor showed a Nernstian slope of 59.5 mV decade−1 in a linear range from 3.2 × 10−7 mol L−1 to 1 × 10−2 mol L−1. This sensor could sufficiently discriminate the target ion from N-methyl-scopine as a possibly interfering official impurity. Selectivity was enhanced by about one order of magnitude compared to other sensors. The proposed sensor was successfully used for the determination of TIO in Spiriva® inhalation powder and compared favourably with the official method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...