Synthesis and polymerization of a new hydantoin monomer with three halogen binding sites for developing highly antibacterial surfaces†
Abstract
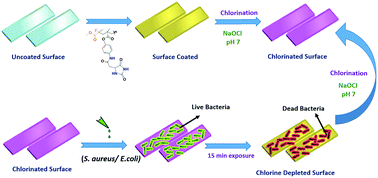
N-Halamine-based antibacterial polymers play a significant role in controlling microbe-associated surface contamination. Hydantoin-containing polymers are usually synthesized by tethering polymerizable moieties to 5,5′-dialkyl hydantoin. However, such approaches sacrifice the imide hydrogen in the molecule, thereby restricting the halogen capture only to the amide nitrogen. In this paper, we report the synthesis of a novel polymerizable hydantoin monomer containing one more amide group in addition to the amide and imide groups already present in hydantoin to maximize the halogen capture and hence its antibacterial activity. The synthesized monomer was copolymerized with methyl methacrylate (MMA) and styrene. The monomer and its copolymers were characterized using 1H and 13C NMR, HRMS, FTIR, XPS, TGA, DTA and GPC. The oxidative chlorine content of the copolymers ranged from 0.9% to 1.21%. The polymers were spin coated onto glass surfaces to study their antimicrobial potential. The polymer-coated glass surfaces exposed to both Gram positive S. aureus and Gram negative E. coli bacteria using standard protocols showed total kill of the bacteria within 15 minutes of exposure. These new hydantoin polymers showed highly superior antibacterial activities compared to many such polymers reported so far in the literature.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...