Coproduction of succinic acid and cadaverine using lysine as a neutralizer and CO2 donor with l-lysine decarboxylase overexpressed Escherichia coli AFP111†
Abstract
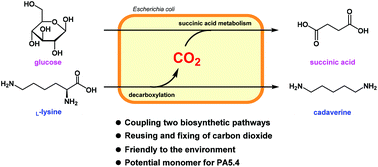
In the biologic production of succinic acid or cadaverine, an alkali or acid is used for neutralization during the production process and for dissociation during purification, leading to the generation of significant levels of waste salt. Furthermore, extra CO2 is required for succinic acid production, while CO2 is a waste byproduct of cadaverine production from lysine. This study aimed to combine succinic acid fermentation with cadaverine production. Two products of lysine decarboxylation, cadaverine and CO2, are subsequently used for succinic acid neutralization and fermentation, respectively. First, L-lysine decarboxylase was successfully overexpressed in a succinic-acid-producing strain (E. coli AFP111) without a decrease in succinic acid production. Then, a pH-dependent coproduction process was developed using succinic acid and L-lysine as acidic and basic neutralizers, respectively. To combine succinic acid and cadaverine production, L-lysine decarboxylase activity, culture pH and CO2 release rate were optimized. Under the optimized cultivation conditions, 21.2 g L−1 of succinic acid and 22.0 g L−1 of cadaverine were obtained without pH adjustment or CO2 supplementation. This process demonstrates benefits for the coproduction of an organic acid and alkali as substrates for polyamide monomers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...