Graphitization of Miscanthus grass biocarbon enhanced by in situ generated FeCo nanoparticles†
Abstract
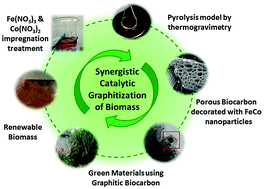
Catalytic graphitization of biocarbon prepared from Miscanthus grass was possible through chemical treatment with iron(III) nitrate, Fe(NO3)3, and cobalt(II) nitrate, Co(NO3)2. The pyrolysis monitoring, until the temperature of 900 °C, permitted for the primary analysis of the effects of the generated catalysis species on biomass degradation. Then both Raman spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction (XRD) allowed for the observation of microstructural changes between the samples treated with metal catalysts and the untreated samples. The samples treated with both iron and cobalt nitrates are twice as efficient at forming ordered graphite than the treated sample with the catalysts used separately. This may be due to FeCo nanoparticles generated in situ during pyrolysis. These results show that the morphology and allotropy of renewable biocarbon can be tailored in such a way that it can be applied to design smart materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...