Synthesis and properties of MoCl4 complexes with thio- and seleno-ethers and their use for chemical vapour deposition of MoSe2 and MoS2 films†
Abstract
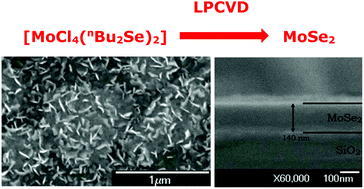
Treatment of trans-[MoCl4(MeCN)2] with L (L = Me2S, Me2Se, THT, ½MeSCH2CH2SMe) in CH2Cl2 solution, or reaction of MoCl5 with excess L′ (L′ = nBu2S, nBu2Se, ½MeSCH2CH2SMe, ½iPrSCH2CH2SiPr, ½MeSCH2CH2CH2SMe, ½MeSeCH2CH2CH2SeMe) in MeCN, produces the Mo(IV) complexes, [MoCl4(L)2] and [MoCl4(L′)2], respectively, in good yield. The new complexes have been characterised by IR and UV-vis spectroscopy, elemental analysis and magnetic measurements, whilst crystal structure analyses of trans-[MoCl4(Me2S)2], cis-[MoCl4{RS(CH2)2SR}] (R = Me, iPr) and cis-[MoCl4{MeS(CH2)3SMe}] confirmed their identities and distorted octahedral geometries. The potential of [MoCl4(nBu2E)2] (E = S, Se) as the first examples of molybdenum halide derived single source CVD precursors for the growth of MoE2 thin films was first probed by TGA, which showed multi-step decomposition processes, with the masses of the final residues consistent with MoSe2 (E = Se) and MoCl4 (E = S), respectively. Low pressure CVD experiments conducted at 750 °C (E = S) and 525 °C (E = Se) gave silvery and golden yellow films, respectively. Grazing incidence and in plane XRD data confirmed these to be 2H-MoE2, whilst the texture of the MoSe2 was investigated using pole figure measurements. SEM and EDX data, optical and Raman data on the films are also reported.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...