The investigation of the electrocatalytic and corrosion behavior of a TiO2–RuO2 anode modified by graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide nanosheets via a sol–gel method
Abstract
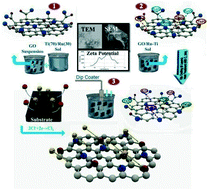
A unique electrocatalyst composed of a dimensionally stable anode (DSA) of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide combined with RuO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles has been synthesized on a titanium substrate through a facile aqueous sol–gel method. The surface morphology, microstructure and composition of the coatings were investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). The contribution of the graphene compounds into the anode composition to improve the corrosion and electrocatalytic features was investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV), polarization measurements, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and an accelerated stability test (AST). The most efficient anode passed the maximum electrical charge at about 145.2 mC cm−2, which was 4.5 times higher than the RuO2–TiO2 (RT) coating, in 0.5 M NaCl + 1 M H2SO4 solution and it was found that the specific current density per unit of the actual surface area (is) ratio of chlorine and oxygen evolution for the optimized electrode was about 3 times higher than the RT electrode which indicates the considerable selectivity behavior of this electrode. The charge transfer resistance of the novel DSA reduced to 2.39 kΩ, while the stability and coating lifetime was improved to 7530 h at j = 1.2 A cm−2 which illustrates that graphene oxide can be used to improve the electrocatalytic performance of DSA anodes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...