A comparative study of the structure, stability and energetic performance of 5,5′-bitetrazole-1,1′-diolate based energetic ionic salts: future high energy density materials
Abstract
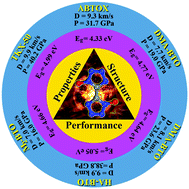
Developing novel energetic materials of high detonation performance and low sensitivity is one of the primary objectives related to explosive research. By employing ab initio calculations, a series of energetic ionic salts based on 5,5′-bitetrazole-1,1′-diolate (BTO) were thoroughly investigated to understand the structure–property–performance interrelationship. The physicochemical and detonation characteristics of these energetic ionic salts including structural, electronic, vibrational and performance parameters (heats of formation, detonation pressures, and detonation velocities) were discussed in detail. The strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding environment between the BTO2− anion and various cations is mainly responsible for prominent detonation performance and enhanced molecular stability. Such strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds are observed in hydrazine and hydroxylammonium cations compared to other cations. To predict an accurate band gap, electronic band structures of the studied energetic ionic salts (EIS) were calculated using the HSE06 hybrid functional and they are found to be wide band gap insulators with a bandwidth ranging from 4.33–5.05 eV. Careful inspection of various EIS revealed that the hydroxylammonium and hydrazine cations produce the highest density relative to other cations when combined with the BTO anion. The detonation characteristics of BTO2− are computed using EXPLO5 code. In particular, HA-BTO and TKX-50 exhibit high detonation pressure (38.85 and 40.23 GPa) and detonation velocities (9.94 and 9.91 km s−1), superior to those of traditional nitrogen-rich energetic materials with moderate sensitivities. These results highlight the importance of hydrogen bonding interactions in designing energetic salts for next-generation explosives, propellants, and pyrotechnics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...