An efficient protocol for computing the pKa of Zn-bound water†
Abstract
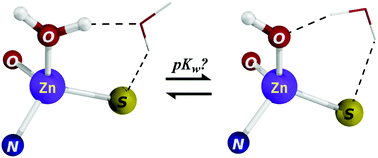
At a given pH, whether a metal-bound water molecule is deprotonated or not can be determined if the pKa of the metal-bound water molecule (denoted pKw) is known. Although protocols/tools to predict the protonation states of titratable amino acid residues and small molecules have been developed, an efficient and accurate method to predict the absolute pKw values of metal complexes is lacking. Here, we present calibrated methods for optimizing the geometries and computing the absolute pKw values of a wide range of Zn2+-complexes containing protein-like ligating groups. We tested 18 different geometry-optimization methods on 19 ultra high-resolution structures of Zn2+ complexes of varying coordination numbers and ligating atoms and 98 methods in reproducing 36 experimental pKw values of diverse Zn2+ complexes in the absence and presence of explicit water molecules. The results underscore the importance of estimating the Zn2+-bound water/hydroxide solvation properly, whereas correcting for the basis set superposition error was not found to be important. The protocol presented can be used to (i) evaluate the geometries of the different Zn2+-sites found in proteins and (ii) to dissect the individual contributions of the various factors modulating the pKw in Zn2+-sites found in proteins. Predicting absolute pKw values in various environments with efficiency and accuracy will indicate when a Zn2+-bound water molecule is deprotonated, thus providing physical insight into the mechanisms of enzyme-catalyzed reactions and the design of drug candidates that can displace a metal-bound water molecule.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...