Design and construction of self-hidden and pH-reversed targeting drug delivery nanovehicles via noncovalent interactions to overcome drug resistance†
Abstract
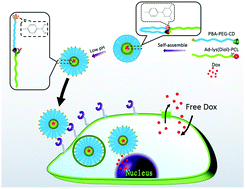
Using the host–guest interaction between β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) and adamantane (Ad), and borate formation between phenylboronic acid (PBA) and cis-diols, a smart pH-responsible targeting drug delivery nanovehicle, PBA–PEG–CD/Ad-lys(Diol)–PCL, was prepared via one-step self-assembly. Under physiological conditions, the targeted PBA function could be restrained by binding PBA with diol components located at the interface of self-assemblies, and hydrophilic PEG segments could be shielded simultaneously. When the environmental pH decreased, the PBA groups could be unbound and exposed on the surface of self-assemblies, leading to recovery of its targeted function, as shown using fluorescence spectroscopy, in vitro cell toxicity, and uptake. Under acidic conditions, PBA–PEG–CD/Ad-lys(Diol)–PCL/Dox showed significantly increased uptake and toxicity toward HepG2 cells in comparison with the control group. The smart vehicles were further utilized to test their efficiency in overcoming drug resistance in chemotherapy. Compared with free Dox, PBA–PEG–CD/Ad-lys(Diol)–PCL delivered six times more Dox into MCF-7/ADR cells and showed greater toxicity toward the ADR cells. As a result, this may be a facile strategy toward constructing efficient targeting vehicles through the rational utilization of noncovalent interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...