The long life-span of a Li-metal anode enabled by a protective layer based on the pyrolyzed N-doped binder network†
Abstract
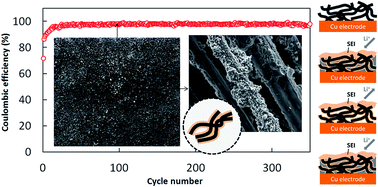
Attempts to utilize lithium metal in secondary batteries are seriously restricted by its uncontrollable side reactions with the electrolyte solvent. Here we utilize a protective porous structure based on the pyrolyzed PAN binder to stabilize the electrolyte/lithium interface to prolong its working life. With the increase of pyrolysis temperatures, the treated PAN fibers possess two mutational points in mechanical properties located at ∼300 & ∼700 °C, and exhibit carbon-like characteristics at ∼400 °C and higher. Compared to the control electrode, the cyclic life-span of the treated electrodes can increase 1.8 times at the first mutational point, and surprisingly rise to 12 & 7 times for the samples pyrolyzed at 400 & 500 °C, then fall back to 1.6 times at the second mutational point. These results reveal that the stable operation of lithium plating/stripping could be provided by the internal interwoven SEI layer grown on the carbon-like binder network with appropriate rigidity. Among the investigated systems, the protective structure treated at 400 °C can stably operate for 350 cycles with an average coulombic efficiency as high as ∼98%, which is the best efficiency recorded for carbonate-based electrolytes to date.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...