Colossal permittivity with ultralow dielectric loss in In + Ta co-doped rutile TiO2†
Abstract
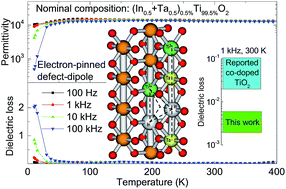
Colossal permittivity (CP) materials have many important applications in electronics but their development has generally been hindered due to the difficulty in achieving a relatively low dielectric loss. In this work, we report an In + Ta co-doped TiO2 material system that manifests high dielectric permittivity and low dielectric loss based on the electron-pinned defect-dipole design. The dielectric loss can be reduced down to e.g. 0.002 at 1 kHz, giving high performance, low temperature dependent dielectric properties i.e. εr > 104 with tan δ < 0.02 in a broad temperature range of 50–400 K. Density functional theory calculations coupled with the defect analysis uncover that electron-pinned defect dipoles (EPDDs), in the form of highly stable triangle-diamond and/or triangle-linear dopant defect clusters with well-defined relative positions for Ti reduction, are also present in the host material for the CP observed. Such a high-performance dielectric material would thus help for practical applications and points to further discovery of promising new materials of this type.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...