pH effects in the acetaldehyde–ammonia reaction
Abstract
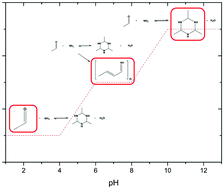
The pH dependency of the reaction of acetaldehyde and ammonia to form the acetaldehyde-ammonia trimer has been studied in detail. The acetaldehyde-ammonia trimer is a molecule of interest in organic synthesis, since it can be used as a substrate in many reactions involving acetaldehyde or ammonia. This trimer is well known in the literature but no references are present so far to describe its formation from ammonia sources other than ammonium hydroxide. The focus of this study is on describing the course of reaction after addition of acetaldehyde to solutions of ammonia and various acids. Products have been analysed by means of 1H-NMR and IR spectroscopy and the complete range of pH values has been covered. Depending on the pH, two reaction regimes can be distinguished. At high pH, only the trimer is formed. In contrast, at low pH, only low quantities of the trimer are produced and the nature of the applied acid has a distinct effect on the reaction outcome. Inorganic acids result in low trimer concentration and high quantity of unreacted ammonia. Polymer formation dominates with simple carboxylic acids. Complex organic acids, such as e.g. maleic or nicotinic acid, lead to comparable quantities of the trimer and acetaldehyde. Based on our results, we propose some adjustments to the traditional reaction scheme developed for acetaldehyde-ammonia trimer formation at high pH.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...