Protein adsorption and desorption behavior of a pH-responsive membrane based on ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer
Abstract
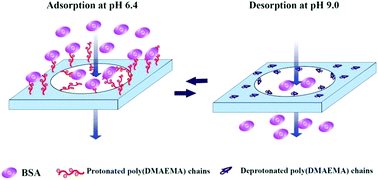
Protein adsorption and desorption behavior was investigated for a pH-responsive ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer (EVAL) membrane with an interconnected porous structure. The transition of electrostatic behavior and conformation change of the poly(dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) (poly(DMAEMA)) chain contributed to the pH-responsive protein adsorption and desorption. Protein adsorption was conducted under acidic and neutral conditions. Protein desorption was conducted under alkaline conditions. The protonated poly(DMAEMA) chain was positively charged and extended into the BSA solution below its pKa, providing a three-dimensional space for BSA adsorption. The maximum static protein adsorption capacity was obtained at pH 6.4. The dynamic adsorption capacities of membrane EVAL10 at 10% and 50% breakthrough were 45 and 99 mg BSA per g of membrane, respectively. The Q50% of membrane EVAL10 was equivalent to 22.6 mg BSA per mL of membrane, almost 95% of the static adsorption capacity. BSA was quickly desorbed from the membrane and 94% recovery of BSA was observed at pH 9.0 in the dynamic desorption process, due to a deprotonated and collapsed conformation of the poly(DMAEMA) chains. The dynamic adsorption capacity of the membrane did not change significantly after four sequential cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...