A novel macroporous polymer–inorganic nanocomposite as a sorbent for pertechnetate ions
Abstract
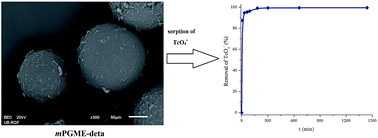
A novel magnetic macroporous poly(glycidyl methacrylate-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) (mPGME) was prepared by suspension copolymerization and functionalized with diethylenetriamine (mPGME-deta). The samples were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis, mercury porosimetry, scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), atomic force microscopy (AFM) and SQUID magnetometry. The sorption behavior of mPGME-deta toward pertechnetate ions (TcO4−) from aqueous solution was studied. Experimental results indicated relatively fast TcO4− sorption kinetics that depends on pH and ionic strength, with a high removal efficiency of 99% within 180 min in the pH range 3.0–5.0. The pseudo-second-order model yielded the best fit for the kinetic data.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...