Photophysics and redox properties of aza-BODIPY dyes with electron-withdrawing groups†
Abstract
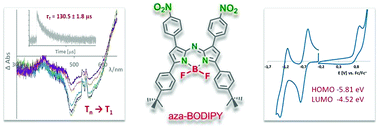
The optical and electrochemical properties are compared for aza-BODIPY dyes that differ by virtue of the substituents at 1,7- and 3,5-positions of the aza-BODIPY backbone. In particular, the impact of highly electron-withdrawing nitro substituents on these properties is of consideration. The aza-BODIPYs studied exhibit a broad absorption band spanning from ca. 600 nm to ca. 700 nm – a spectral region that is highly sought after for biomedical applications – and possess high molar absorption coefficients (ε) ranging from 64 000 [M−1 cm−1] to 85 000 [M−1 cm−1] in THF. The compounds studied are weakly emissive as non-radiative decay is the predominant way of the excited state energy dissipation. Exemplarily, the fluorescence quantum yields (Φfl) measured in THF were in the range of 0.03 to 0.06 for the aza-BODIPYs studied. Transient absorption experiments revealed T1 → Tn absorption spanning from ca. 400 nm to ca. 600 nm and allowed determination of the triplet state lifetimes. The estimated triplet lifetimes (τT) in deaerated THF ranged from 77 µs to 130 µs. As estimated by the CV/DPV measurements, all aza-BODIPYs studied exhibited one irreversible oxidation and two quasi-reversible reductions. Estimation of the EHOMO gave a value of ca. −5.8 eV while the ELUMO was found to be located at ca. −4.5 eV. Extremely high photostability and thermal robustness up to approximately 300 °C were found for the nitro-substituted aza-BODIPYs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...