Selective detection of inorganic phosphates in live cells based on a responsive fluorescence probe†
Abstract
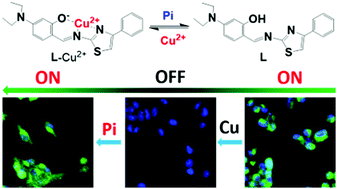
In this work, we have designed and synthesized a new 4-phenylthiazole-Cu2+ ensemble, L-Cu2+, as a fluorescence probe for the quantitative detection of inorganic phosphates (Pi) in aqueous and live cells. A fluorescent ligand, 2-((4-phenylthiazole-2-imino)methyl)-5-diethylaminophenol (L), was synthesized and its chemical structure was well characterized. L exhibited a high affinity (Ka = 3.27 × 105 M−1) and specificity for Cu2+ ions through a 1 : 1 stoichiometry to form a fluorescence sluggish L-Cu2+ ensemble. This L-Cu2+ ensemble was then employed as a turn-on fluorescence probe for the detection of Pi. Spectroscopic studies revealed that L-Cu2+ possesses excellent tolerance to other common interference anions, and in particular to AMP, ADP, ATP, PPi. The detection limit of L-Cu2+ to Pi was determined to be 0.2 μM. The desirable features of L-Cu2+, such as high specificity and sensitivity and low cytotoxicty, enable its application in the detection of Pi in biological samples. Fluorescence imaging of Pi in live MDA-MB-231 cells was conducted to demonstrate its capability in bioimaging applications. Quantitative analysis of Pi in single cells was then demonstrated using flow cytometry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...