Side chain-functionalized aniline-derived ursolic acid derivatives as multidrug resistance reversers that block the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway and cell proliferation†‡
Abstract
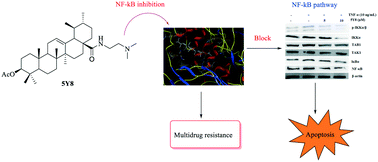
A series of inhibitors of NF-κB based on ursolic acid (UA) derivatives containing functionalized aniline or amide side chains were synthesized and evaluated for inhibition of NF-κB as well as their antitumor effects. These compounds exhibited significant inhibition activity toward NF-κB with IC50 values at micromolar concentrations in the NCI-H460 lung adenocarcinoma cell line. A docking study of the most active compound 5Y8 revealed key interactions between 5Y8 and the active site of NF-κB in which the functionalized amide moiety at the C-28 position and an ester group at the C-3 position were important for improving the activity. In particular, compound 5Y8 appeared to be the most potent compound against the NCI-H460 cell line, and displayed similar efficiency in drug-sensitive versus drug-resistant cancer cell lines, at least partly, by blocking the NF-κB signaling pathway and inducing apoptosis. Mechanistically, compound 5Y8 might trigger the apoptotic signaling pathway. Thus, the rational design of UA derivatives with functionalized aniline or amide side chains offers significant potential for the discovery of a new class of NF-κB inhibitors with the ability to induce apoptosis and reverse multidrug resistance in the NCI-H460 lung adenocarcinoma cell line.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...