Twisting induces ferromagnetism in homometallic clusters†
Abstract
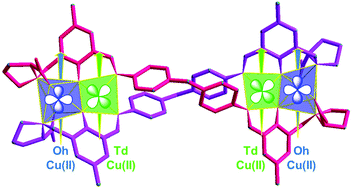
A helical chiral cluster bridging two sets of Cu2 units is reported. The two double-stranded ligands induce a distorted tetrahedral environment for one of the two copper(II) ions whereas the second one remains in a standard octahedral environment. Magnetic measurements and wavefunction calculations demonstrate that the copper(II) centres are ferromagnetically coupled (J = 7.7 cm−1). This ligand-driven ferromagnetic interaction thus appears as a proof-of-concept of an innovative strategy towards high-spin clusters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...