In situ ligand exchange-mediated 0D/1D transformation of a polyoxovanadate†
Abstract
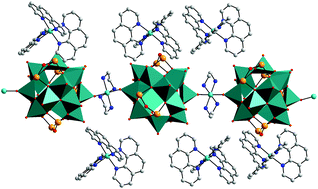
The antimonato-polyoxovanadate {NiII(en)3}3[VIV15SbIII6O42(H2O)]·ca.15H2O was utilized as a synthon for the solvothermal in situ generation of the new compound {NiII(phen)3}2[{NiII(en)2}VIV15SbIII6O42(H2O)]·19H2O, a rearrangement induced by ligand metathesis. While in the precursor structure cations and anions are isolated, the solid-state structure of the product is characterized by 1D chains consisting of alternating [V15Sb6O42(H2O)]6− cluster shells and [Ni(en)2]2+ units covalently linked to neighboring clusters via terminal oxygen atoms. Water clusters composed of sixteen hydrogen-bonded H2O molecules are located in void spaces of the structure. The magnetic properties indicate weak antiferromagnetic interactions of the bridging Ni2+ center and adjacent polyoxovanadate anions, as well as small magnetic anisotropy of the individual Ni2+ centers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...