Biodegradable injectable polymer systems exhibiting a longer and controllable duration time of the gel state†
Abstract
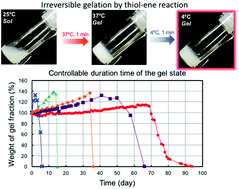
Here, we report biodegradable temperature-triggered covalent gelation systems exhibiting a longer and controllable duration time of the gel state by a “mixing strategy” utilizing a thiol–ene reaction. We synthesized a tri-block copolymer of poly(caprolactone-co-glycolic acid) and PEG (tri-PCG) as a temperature-responsive injectable polymer (IP) and attached acryloyl groups on both termini (tri-PCG-Acryl). A tri-PCG micelle solution containing hydrophobic hexa-functional polythiol (Solution-A) and a tri-PCG-Acryl micelle solution (Solution-B) were mixed together. After mixing, the solution was still in the sol state at r.t., but exhibited an irreversible sol-to-gel transition in response to temperature. The duration time of the gel state while soaking in PBS could be altered from 1 day to 93 days by changing the mixing ratio of Solution-A/B. The physical strengths of the hydrogels were also controllable by changing the mixing ratio. The IP system showed good biocompatibility and a long duration time of the gel state after subcutaneous implantation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...