A sensitive and selective electrochemiluminescent sensor for dopamine based on the inhibition of dual-stabilizer-capped CdS quantum dot electrochemiluminescence
Abstract
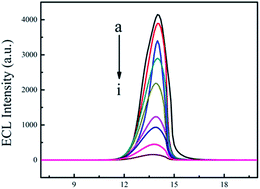
An electrochemiluminescent (ECL) sensor with dual-stabilizer-capped CdS quantum dots (QDs) as an ECL emitter was constructed and used for the determination of dopamine (DA). The dual-stabilizer-capped CdS QDs were covalently immobilized onto a p-aminobenzoic acid (ABA) modified glass carbon electrode with 1,3-propylene amide (PDA) as a link molecule. The introduction of multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) into the electrode increased the ECL signal to 1.5 times. The proposed sensor produced a strong ECL signal under −1.4 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) and the signal could be quenched by DA which can be used for the detection of DA in the range of 5.0 × 10−9 to 5.0 × 10−6 mol L−1. The detection limit was 1.6 × 10−9 mol L−1. This strategy provides a potential approach to constructing ECL sensors for other biomolecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...