Chiral separation of methadone in exhaled breath condensate using capillary electrophoresis†
Abstract
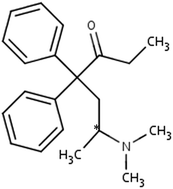
Breath analysis is a potential tool for monitoring the status of respiratory or systemic disorders. Non-invasive sampling techniques and reliable analytical methods for quantification of drugs of abuse are needed in therapeutic drug monitoring, clinical, sport medicine, and forensic applications. We assessed the effectiveness of exhaled breath condensate (EBC) as an alternative specimen to urine and blood in terms of ease of collection and matrix simplicity. A simple electrodriven separation method using a capillary electrophoresis system is presented for quantification of methadone enantiomers after direct injection of EBC in sample stacking mode. Stereoselective determination of methadone is needed because of the significant variation of the inter-subject enantiomeric ratio in patients receiving racemate. Our study is focused on the use of EBC as a readily available biological sample to monitor methadone levels with good patient compliance. However, the inter-correlation of methadone concentrations between EBC and serum or urine is not established and is investigated in the present work. Serum and urine samples from the patients were analyzed after microextraction using the developed method. The proposed method was validated according to US FDA guidelines over the concentration range of 0.15–5 μg mL−1 for each enantiomer of methadone. Inter- and intra-day precisions and accuracies were within the acceptable limit (20% for biological determinations). The recoveries ranged from 86 to 102% and the method was specific for routine analysis of methadone. Small-volume EBC samples from seven patients under methadone maintenance therapy were analyzed using the proposed method in which the concentrations of R- and S-enantiomers varied between 0.16 and 1.06 μg mL−1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...