Achieving biosensing at attomolar concentrations of cardiac troponin T in human biofluids by developing a label-free nanoplasmonic analytical assay†
Abstract
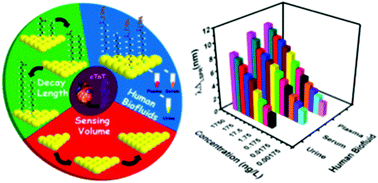
Acute myocardial infarction (heart attack) is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States (Dariush et al., Circulation, 2015, 131, e29–e322). This highlights the need for early, rapid, and sensitive detection of its occurrence and severity through assaying cardiac biomarkers in human fluids. Herein we report chip-based fabrication of the first label-free, nanoplasmonic biosensor to assay cardiac troponin T (cTnT) in human biofluids (plasma, serum, and urine) with high specificity. The sensing mechanism is based on the adsorption model that measures the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) wavelength shift of anti-cTnT functionalized gold triangular nanoprisms (Au TNPs) induced by a change of their local dielectric environment upon binding of cTnT. We demonstrate that controlled manipulation of the sensing volume and decay length of Au TNPs together with an appropriate surface functionalization and immobilization of anti-cTnT onto TNPs allows us to achieve a limit of detection (LOD) of our cTnT assay at attomolar concentration (∼15 aM) in human plasma. This LOD is at least 50-fold more sensitive than that of other label-free techniques. Furthermore, we demonstrate excellent sensitivity of our sensors in human serum and urine. Importantly, our chip-based fabrication strategy is extremely reproducible. We believe our powerful analytical tool for detection of cTnT directly in human biofluids using this highly reproducible, label-free LSPR sensor will have great potential for early diagnosis of heart attack and thus increase patients’ survival rate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...