Characterization and application studies of ProxyPhos, a chemosensor for the detection of proximally phosphorylated peptides and proteins in aqueous solutions†
Abstract
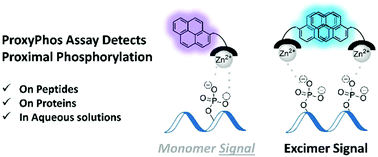
Proximal phosphorylation on proteins appears to have functional significance and has been associated with several diseases, including Alzheimer's and cancer. While much remains to be learned about the role of proximal phosphorylation in biological systems, no simple and/or affordable technique is available for its detection. To this end, we have previously developed a ProxyPhos chemosensor, which detects proximally phosphorylated peptides and proteins over mono- and non-phosphorylated motifs in aqueous solutions. In this follow-up work, we performed extensive characterization of peptide and protein ProxyPhos assay conditions to achieve enhanced detection, and further explored the selectivity of ProxyPhos, and its potential off-targets. As a result of characterization studies, selective sensing of proximally phosphorylated over mono-phosphorylated peptides and proteins was achieved. Moreover, studies demonstrated that ProxyPhos was compatible with the detection of all commonly phosphorylated residues (i.e. tyrosine, serine and threonine residues). Under optimized conditions, ProxyPhos efficiently discriminated between peptides derived from the activated (proximally phosphorylated, disease-relevant) and inactive (mono-phosphorylated) forms of JAK2, SYK and MAPK1 kinases. In addition, ProxyPhos can be used to probe phosphatase activity on peptides and proteins via detecting changes in proximal phosphorylation, demonstrating immediate utility of this chemosensing system.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...