Preparation of fine particles of sheelite-monoclinic phase BiVO4via an aqueous chelating method for efficient photocatalytic oxygen evolution under visible-light irradiation†‡
Abstract
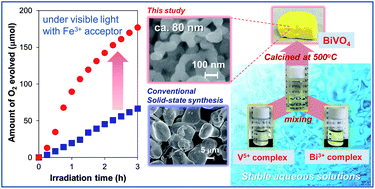
In this paper, we introduce a new synthesis method to prepare fine particles of BiVO4 with a scheelite-monoclinic (s-m) phase, which is known as the most favorable crystal phase for photocatalytic water oxidation (O2 evolution) under visible light irradiation, based on a coordination chemistry approach in water. Stable aqueous solutions that contain both Bi3+ and V5+ complexes were prepared by simply mixing two aqueous solutions in which each cation was stabilized with an appropriate chelating agent. The use of chelating agents (glycolic acid (gly), L(+)-tartaric acid (tart), citric acid (cit), or ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (edta)) was effective to form stable V5+ complexes from NH4VO3. On the other hand, only the use of two equivalents of edta with Bi(NO3)3·5H2O was effective to stabilize the Bi3+ complex in water, while the use of other ligands resulted in precipitations. Evaporation of the aqueous solution containing the stable Bi3+ and V5+ complexes and subsequent calcination in air at 500 °C yielded s-m BiVO4 particles smaller than 300 nm, which were much smaller than BiVO4 particles prepared via conventional solid-state reactions (1–10 μm). In particular, the BiVO4 particles that were prepared with the tart ligand for V5+ stabilization possessed the smallest size (∼80 nm) and exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity for O2 evolution from an aqueous solution containing an electron acceptor (Ag+ or Fe3+) under visible-light irradiation. These results strongly suggested that the tart ligand effectively suppresses particle growth during the crystallization process and thereby affords small BiVO4 particles with high crystallinity, both of which are necessary to achieve highly efficient photocatalysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...