Structure and properties of tough polyampholyte hydrogels: effects of a methyl group in the cationic monomer
Abstract
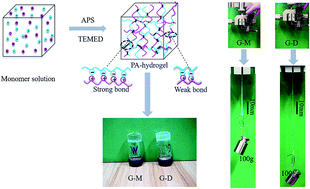
Two types of polyampholyte (PA) hydrogels are successfully synthesized by a facile one-step random copolymerization method using an ammonium peroxydisulfate (APS)/aliphatic amine [N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylenediamine (TEMED)] redox system. Two cationic monomers, differing only slightly by the presence of a methyl group, [2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl]trimethylammonium chloride (MATAC) and acryloyloxethyltrimethylammonium chloride (DMAEA-Q), are used to fabricate two hydrogels with the same anionic monomer. The obtained hydrogels show large differences in their mechanical properties. The G-M hydrogels containing MATAC are much stiffer and stronger than the G-D hydrogels containing DMAEA-Q. Particularly, the G-D gels are super stretchable, with a fracture strain of 12 600%, a work of extension at fracture of 27.8 MJ m−3, and a stress of 0.5 MPa. The mechanical properties of these hydrogels are comparable to, or even better than, those of the hydrogels prepared under stricter conditions via UV polymerization. The very slight steric bulk of the methyl group exhibits significant effects not only on the strength and distribution of the ionic bonds, but also on the microstructures of the G-M and G-D hydrogels. Although G-M contains more hydrophobic methyl groups, its water content and surficial hydrophilicity are higher than those of G-D. Moreover, the polymer network of G-M stacks more homogenously and stereoscopically with stronger interactions. The results obtained in this study will increase the understanding of structures and properties of tough hydrogels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...