Defects induced changes in the electronic structures of MgO and their correlation with the optical properties: a special case of electron–hole recombination from the conduction band†
Abstract
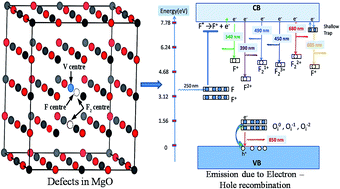
A detailed investigation on different defects from induced emission characteristics in MgO, which are responsible for the multicolor emissions and lasing property of that material, is presented in this report. The color centers are characterized by absorption spectroscopy, decay kinetics, and a TRES study. Various defect centers such as oxygen vacancies (e.g., F, F+, 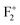 ,
, 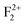 ,
, 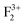 ), cationic vacancies (
), cationic vacancies (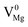 ,
, 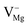 ,
, 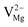 ), interstitial oxygen (
), interstitial oxygen (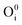 ,
, 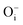 ,
, 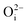 ), Schottky defect
), Schottky defect 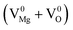 , etc., create different electronic states inside the wide band gap. Density Functional Theory (DFT) based calculation was performed for these defect centers to characterize their ground electronic states inside the band-gap. In MgO, a photo ionization process of the F center is involved at an excitation wavelength of 250 nm, followed by the equation F + hν ↔ F+ + e. The released electron in this process may prompt into the conduction band and thereby behaves as a free carrier. Being free, the electron may recombine with different types of positively charged defect centers in addition to the newly formed F+ centers. Thus, different electronic transitions from the conduction band (CB) to the empty ground electronic states of positively charged F- and F2-type centers can be correlated with their observed emission components. Recombination of a hole in the valence band (VB) with a filled electron in the electronic states may also be responsible for some emission behaviors. Thus, an understanding about all the emitting color components due to various defect centers in MgO might be possible by considering those special recombination processes and may also help to remove the long standing contradiction regarding their origin.
, etc., create different electronic states inside the wide band gap. Density Functional Theory (DFT) based calculation was performed for these defect centers to characterize their ground electronic states inside the band-gap. In MgO, a photo ionization process of the F center is involved at an excitation wavelength of 250 nm, followed by the equation F + hν ↔ F+ + e. The released electron in this process may prompt into the conduction band and thereby behaves as a free carrier. Being free, the electron may recombine with different types of positively charged defect centers in addition to the newly formed F+ centers. Thus, different electronic transitions from the conduction band (CB) to the empty ground electronic states of positively charged F- and F2-type centers can be correlated with their observed emission components. Recombination of a hole in the valence band (VB) with a filled electron in the electronic states may also be responsible for some emission behaviors. Thus, an understanding about all the emitting color components due to various defect centers in MgO might be possible by considering those special recombination processes and may also help to remove the long standing contradiction regarding their origin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...