Well-defined quantum dots and broadening of optical phonon line from hydrothermal method†
Abstract
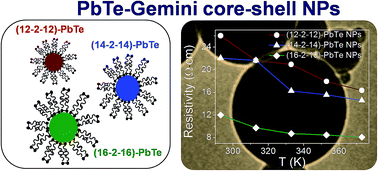
A versatile and facile methodology is presented for size-controlled, lead telluride nanoparticles in the presence of highly hydrophobic cationic gemini surfactants (12–2–12, 14–2–14 and 16–2–16) as capping/stabilizing agents. The optical and electrical properties were examined with attention focused on the cumulative diameter of lead telluride NPs for various stabilizing agents. To explore the influence of surfactants' hydrophobicity on the shape and size of lead telluride NPs, the microstructure of lead telluride NPs was investigated via transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Core–shell nanoparticles were characterized by using XRD, near-IR, PL and Raman techniques.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...